Lab 5: DHSVM Big Beef Creek
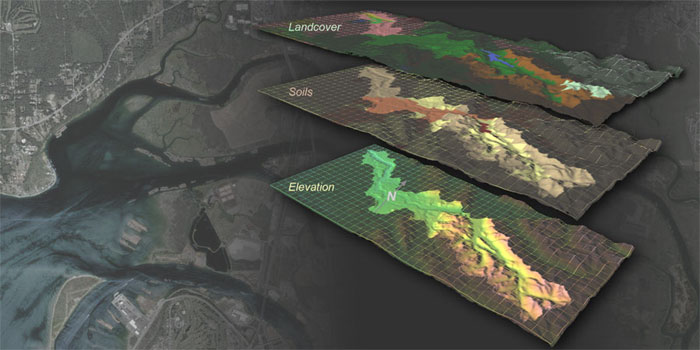
Lab 5: Applying the Distributed Hydrology Soil-Vegetation Model (DHSVM) to Big Beef Creek
This computer lab exercise will explore the application of cutting edge watershed basin models. The Distributed Hydrology Soil Vegetation Model (DHSVM), developed at UW, is a computerized modeling environment that reconstructs the topography, soil, and vegetative properties of a watershed. Using precipitation data, DHSVM is capable of accurately depicting the flow of water throughout a basin, and can also be used to predict the effects of changes in land use and watershed properties.
The Solute Export Model (D-SEM) can be applied to the DHSVM framework to predict the flow of chemicals such as carbon and nitrogen constituents throughout the watershed during varying conditions. During these lab exercises, we will utilize DHSVM and D-SEM in the Hood Canal basin to observe the delivery of Nitrogen from the watershed into Hood Canal, which has implications into the hypoxia of Hood Canal. Furthermore, we will see how Nitrogen fluxes may change under various circumstances such as land use or climate change.
Background Information:
